Carrier RNA
Carrier RNA is a mixture of RNA fragments between 200-3000 nt dissolved in RNA protectant (Cat. No. 4006002).
Description
In the process of column purification of trace (ng-level) nucleic acids, such as viral RNA purification, viral DNA purification, and DNA extraction from criminal case samples, the binding and elution efficiency of trace nucleic acids on the spin column is extremely poor, resulting in insufficient PCR template recovery, and ultimately the detection fails.
The addition of Carrier RNA to the nucleic acid purification system can improve the recovery efficiency of trace nucleic acids by more than 10 times, and at the same time, due to the presence of Carrier RNA, it can also protect the trace RNA template and reduce the chance of RNase attack on the trace RNA template. Carrier RNA is an indispensable component of trace nucleic acid purification, such as viral RNA purification.
Protocol
Add 1–5 μl Carrier RNA to the lysate of each purification system. The resulting trace nucleic acids containing Carrier RNA can be used directly in PCR or RT-PCR reactions.
Experimental data
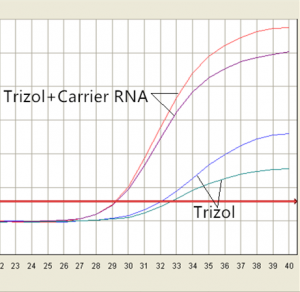
Figure 1: Amplification plot of HCV gene.
Viral RNA extraction from hepatitis C virus (HCV) serum (103 copies/ml) with Simgen Trizol reagent after adding Carrier RNA. Viral RNA was reverse transcribed, and cDNA was used as a template for qPCR amplification.
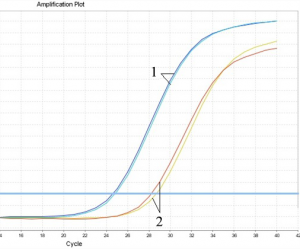
Figure 2: Amplification plot of SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus.
Viral RNA extraction from SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus serum (106 copies/ml) with Simgen Viral Nucleic Acid Extraction Kit. Viral RNA was reverse transcribed, and cDNA was used as a template for qPCR amplification.
1: Carrier RNA added. 2: Without Carrier RNA. Compared with the extraction method without carrier RNA, the CT value of Carrier RNA added was reduced by about 3~4 CT values.